NEWCASTLE.- Scientists have created a novel technology that can help to tackle climate change and address the global energy crisis.
Northumbria University's Dr. Shafeer Kalathil is among a team of academics behind the project, which uses a chemical process that converts sunlight, water and carbon dioxide into acetate and oxygen to produce high-value fuels and chemicals powered by renewable energy.
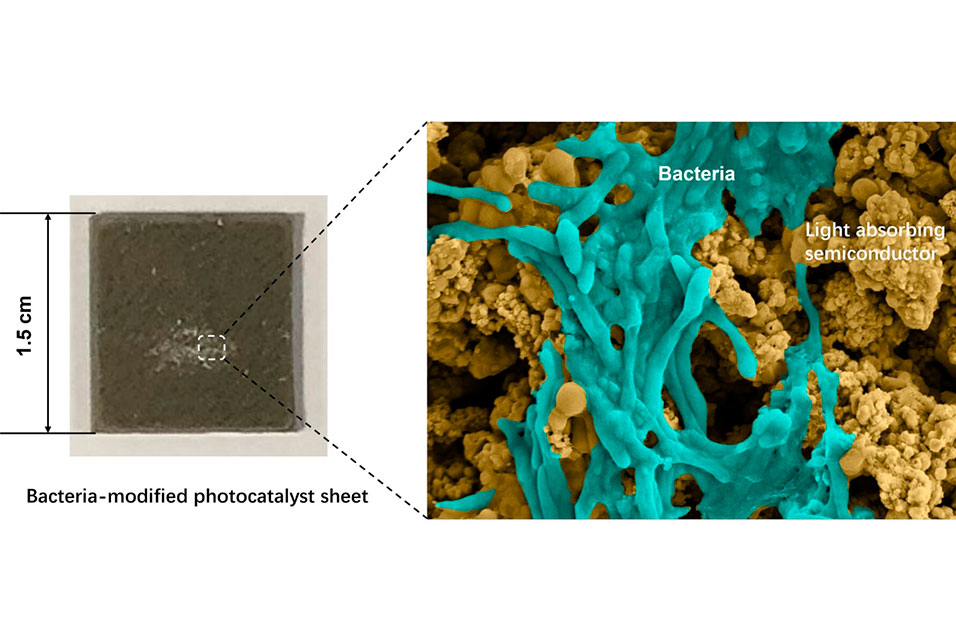
As part of the process, bacteria are grown on a synthetic semiconductor device known as a photocatalyst sheet, which means that the conversion can take place without the assistance of organic additives, creation of toxins or use of electricity.
The aim of the project is to curtail the rise in atmospheric CO2 levels, secure much-needed green energy supplies and alleviate the global dependence on fossil fuels. A paper detailing the findings of the team's research has been published in Nature Catalysis.
Dr. Kalathil, Vice Chancellor's Senior Fellow, is working on the project with Erwin Reisner, Professor of Energy and Sustainability at the University of Cambridge, Dr. Qian Wang, associate professor at Nagoya University in Japan, and partners from Newcastle University.
Dr. Kalathil says that "several incidents have demonstrated the fragility of the global energy supply, such as recent soaring gas prices in UK, the outbreak of conflicts and civil wars in the Middle East and the ecological and humanitarian threat of a nuclear meltdown in Fukushima, Japan. The search for alternative energy sources is therefore of major global importance."
"Our research directly addresses the global energy crisis and climate change facing today's society. We need to develop new technologies to address these grand challenges without further polluting the planet we live on."
"There has been an increase in electricity generation from renewable sources such as wind and solar, but these are intermittent in nature. To fill the gap when the wind doesn't blow or the sun doesn't shine, we need technologies that can create storable fuels and sustainable chemicals. Our research addresses this challenge head on."
"As well as securing additional much-needed energy supplies, our sustainable technology can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and play a key role in the global drive to achieve net zero."
The project was supported by funding from the European Research Council, UK Research and Innovation, and Research England's Expanding Excellence in England Fund, which supports higher education research units and departments to expand and increase their activity. The Research England grant was secured via the Hub for Biotechnology in the Built Environment (HBBE), a joint initiative between Northumbria and Newcastle University, which has received a total of £8 million from Research England to conduct project work. Launched in August 2019, the HBBE develops biotechnologies to create environmentally friendly buildings that can metabolize waste, reduce pollution, generate sustainable energy and improve human health and well-being.
Dr. Kalathil, who is heavily involved with the HBBE, says that "the aims of the HBBE fit with what we're trying to achieve with our research—to address key environmental concerns facing our society today and in the future. This emerging field of research represents an interdisciplinary approach that combines the strengths of microbes, synthetic materials and analytical techniques for chemical transformation, and provides an excellent platform to produce high-value, environmentally friendly fuels and chemicals at scale. We're already in discussions with international chemical manufacturers and cosmetics producers, and the ultimate aim is to develop our technology on a commercial scale."