WASHINGTON, DC.- The right indoor lighting can help set the mood, from a soft romantic glow to bright, stimulating colors. But some materials used for lighting, such as plastics, are not eco-friendly. Now, researchers reporting in
ACS Nano have developed a bio-based, luminescent, water-resistant wood film that could someday be used as cover panels for lamps, displays and laser devices.
Consumer demand for eco-friendly, renewable materials has driven researchers to investigate wood-based thin films for optical applications. However, many materials developed so far have drawbacks, such as poor mechanical properties, uneven lighting, a lack of water resistance or the need for a petroleum-based polymer matrix. Qiliang Fu, Ingo Burgert and colleagues wanted to develop a luminescent wood film that could overcome these limitations.
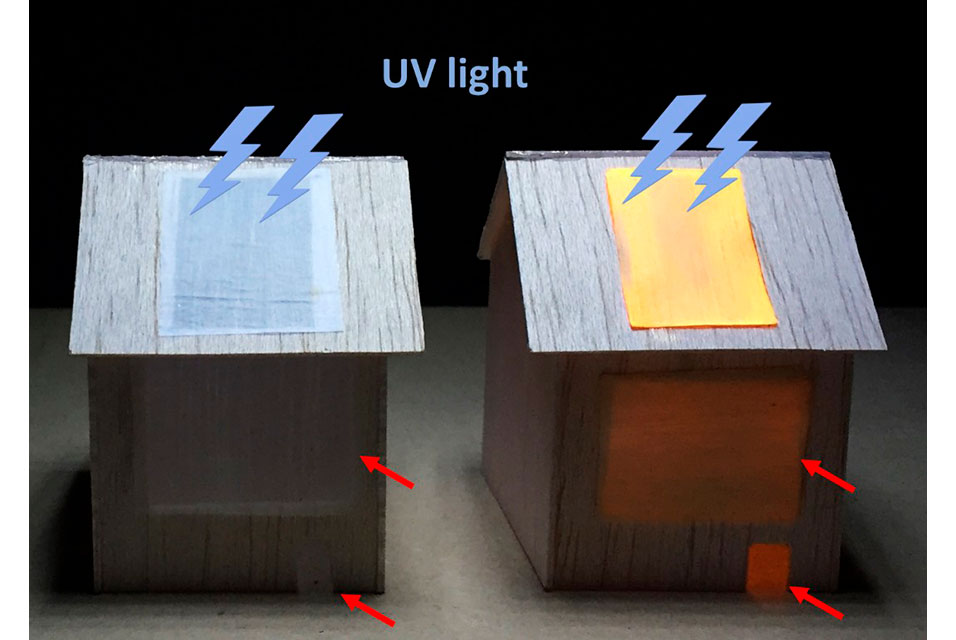
The researchers treated balsa wood with a solution to remove lignin and about half of the hemicelluloses, leaving behind a porous scaffold. The team then infused the delignified wood with a solution containing quantum dots –– semiconductor nanoparticles that glow in a particular color when struck by ultraviolet (UV) light. After compressing and drying, the researchers applied a hydrophobic coating. The result was a dense, water-resistant wood film with excellent mechanical properties. Under UV light, the quantum dots in the wood emitted and scattered an orange light that spread evenly throughout the film’s surface. The team demonstrated the ability of a luminescent panel to light up the interior of a toy house. Different types of quantum dots could be incorporated into the wood film to create various colors of lighting products, the researchers say.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Royal Society of New Zealand Te Apārangi and the New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment.