KYOTO.- Scanning lasers -- from barcode scanners at the supermarket to cameras on newer smartphones -- are an indispensable part of our daily lives, relying on lasers and detectors for pinpoint precision.
Distance and object recognition using LiDAR -- a portmanteau of light and radar -- is becoming increasingly common: reflected laser beams record the surrounding environment, providing crucial data for autonomous cars, agricultural machines, and factory robots.
Current technology bounces the laser beams off of moving mirrors, a mechanical method that results in slower scanning speeds and inaccuracies, not to mention the large physical size and complexity of devices housing a laser and mirrors.
Publishing in Nature Communications, a research team from
Kyoto University's Graduate School of Engineering describe a new beam scanning device utilizing 'photonic crystals', eliminating the need for moving parts.
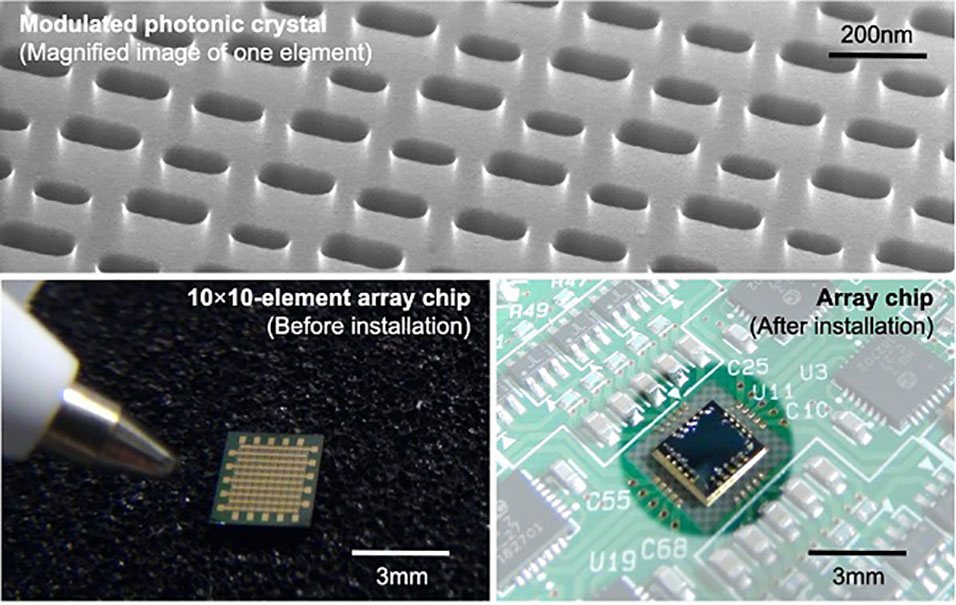
Instead of arranging the lattice points of the crystals in an orderly array, the researchers found that varying the lattice points' shapes and positions caused the laser beam to be emitted in unique directions.
"What results is a lattice of photonic crystals that looks like a slab of Swiss cheese, where each crystal is calculated to emit the beam in a specific direction," explains Susumu Noda, who led the team.
"By eliminating mechanical mirrors, we've made a faster and more reliable beam-scanning device."
Photonic crystal lasers are a type of 'semiconductor laser' whose lattice points can be regarded as nanoscale antennae, which can be arranged to cause a laser beam to be emitted perpendicularly from the surface. But initially the beam would only go in a single direction on a two-dimensional plane; the team needed more area to be covered.
Arranging the antennae positions cyclically resulted in a successful direction change, but a decrease in power output and deformed shape made this solution unviable.
"Modulating the antennae positions caused light emitted from adjacent antennae to cancel each other out," continues Noda, "leading us to try changing antenna sizes."
"Eventually, we discovered that adjusting both position and size resulted in a seemingly random photonic crystal, producing an accurate beam without power loss. We called this a 'dually modulated photonic crystal'."
By organizing these crystals -- each designed to emit a beam in a unique direction -- in a matrix, the team was able to build a compact, switchable, two-dimensional beam scanner without the need for any mechanical parts.
The scientists have successfully constructed a scanner that can generate beams in one hundred different directions: a resolution of 10×10. This has also been combined with a diverging laser beam, resulting in a new type of LiDAR with enhanced scope to detect objects.
The team estimates that with further refinements, the resolution could be increased by a factor of 900: up to a 300×300 resolution range.
"At first there was a great deal of interest in whether a structure that is seemingly so random could actually work," concludes Noda. "We now believe that eventually we will be able to develop a LiDAR system small enough to hold on a fingertip."