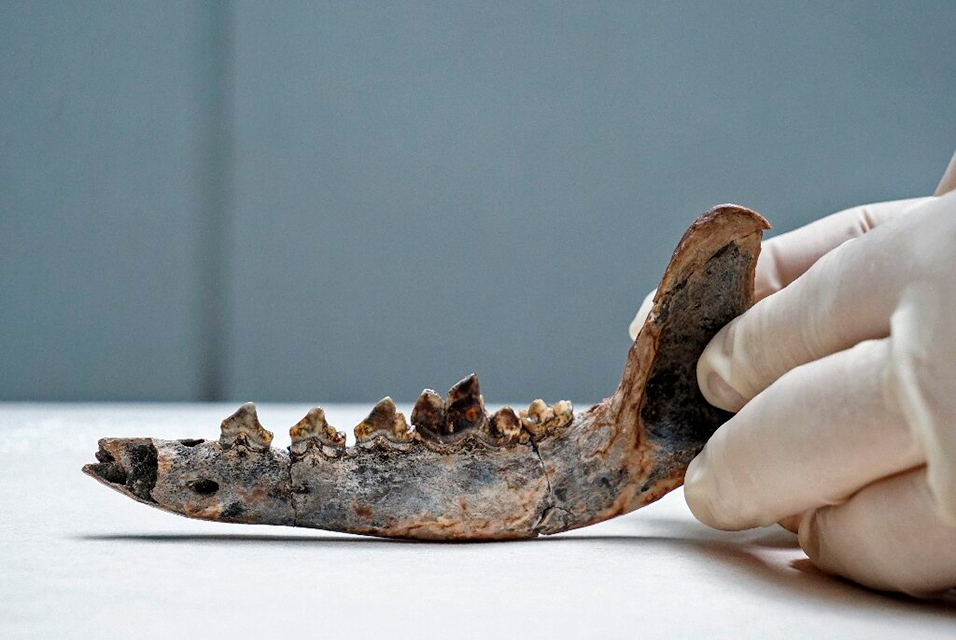
SAN JOSÉ (AFP).- The fossil of a jaw bone could prove that domesticated dogs lived in Central America as far back as 12,000 years ago, according to a study by Latin American scientists.
The dogs, and their masters, potentially lived alongside giant animals, researchers say.
A 1978 dig in Nacaome, northeast Costa Rica, found bone remains from the Late Pleistocene.
Excavations began in the 1990s and produced the remains of a giant horse, Equus sp, a glyptodon (a large armadillo), a mastodon (an ancestor of the modern elephant) and a piece of jaw from what was originally thought to be a coyote skull.
"We thought it was very strange to have a coyote in the Pleistocene, that is to say 12,000 years ago," Costa Rican researcher Guillermo Vargas told AFP.
"When we started looking at the bone fragments, we started to see characteristics that could have been from a dog.
"So we kept looking, we scanned it... and it showed that it was a dog living with humans 12,000 years ago in Costa Rica."
The presence of dogs is a sign that humans were also living in a place.
"We thought it was strange that a sample was classified as a coyote because they only arrived in Costa Rica in the 20th century."
First of its kind
The coyote is a relative of the domestic dog, although with a different jaw and more pointed teeth.
"The dog eats the leftovers from human food. Its teeth are not so determinant in its survival," said Vargas.
"It hunts large prey with its human companions. This sample reflects that difference."
Humans are believed to have emigrated to the Americas across the Bering Strait from Siberia to Alaska during the last great ice age.
"The first domesticated dogs entered the continent about 15,000 years ago, a product of Asians migrating across the Bering Strait," said Raul Valadez, a biologist and zooarcheologist from the National Autonomous University of Mexico.
"There have never been dogs without people," Valadez told AFP by telephone.
The presence of humans during the Pleistocene has been attested in Mexico, Chile and Patagonia, but never in Central America, until now.
"This could be the oldest dog in the Americas," said Vargas.
So far, the oldest attested dog remains were found in Alaska and are 10,150 years old.
Oxford University has offered to perform DNA and carbon dating tests on the sample to discover more genetic information about the animal and its age.
The fossil is currently held at Costa Rica's national museum but the sample cannot be re-identified as a dog without validation by a specialist magazine.
"This dog discovery would be the first evidence of humans in Costa Rica during a period much earlier" than currently thought, said Vargas.
"It would show us that there were societies that could keep dogs, that had food surpluses, that had dogs out of desire and that these weren't war dogs that could cause damage."
© Agence France-Presse