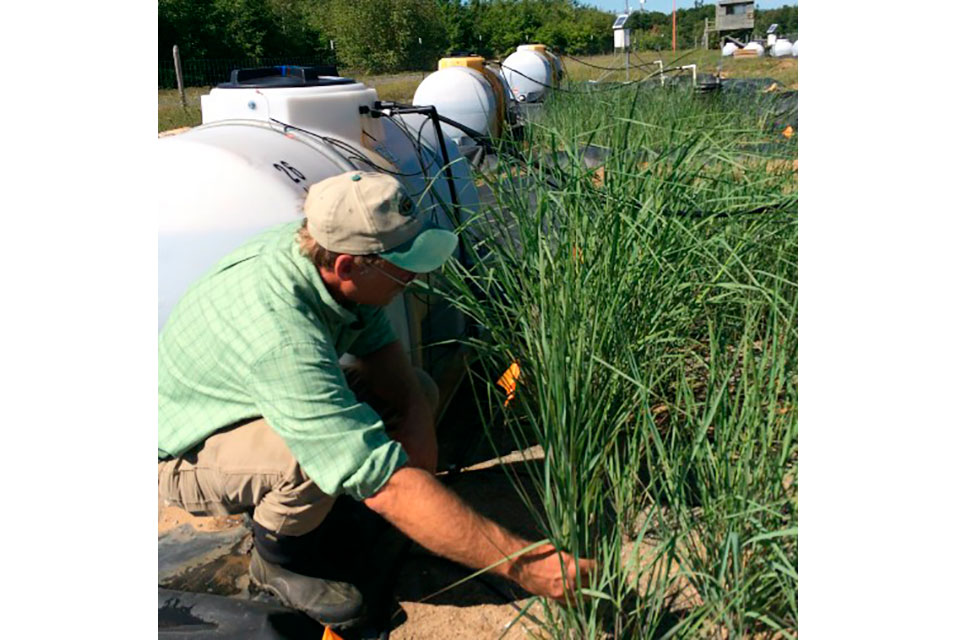
YORK.- The study – led by the
University of York- demonstrates that genetically modified switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) can detoxify residues of the military explosive, RDX, left behind on live-fire training ranges, munitions dumps and minefields.
RDX has been a major component of munitions since WW2 which are still used extensively on military training grounds. This use has now resulted in widespread pollution of groundwater.
Researchers generated the plants by inserting two genes from bacteria able to breakdown RDX. The plants were then grown in RDX contaminated soil on a US military site. The genetically modified grass grew well and successfully degraded RDX to non-detectable levels in their plant tissues.
Pollutants
Study authors, Professor Neil Bruce from the Department of Biology and Director of the Centre for Novel Agricultural Products (CNAP) and Dr Liz Rylott, also from CNAP believe it is the first successful example of the use of a GM plant in-the-field to remove organic pollutants, which are resistant to environmental degradation.
Dr Rylott said: “The removal of the toxic RDX from training ranges is logistically challenging and there is currently a lack of cost-effective and sustainable solutions.
“Our research demonstrates how the expression, in switchgrass, of two bacterial genes that have evolved specifically to degrade RDX give the plants the ability to remove and metabolise RDX in the field at concentrations relevant to live fire military ranges.
“We demonstrated that by inserting these genes into switchgrass, the plant then had the ability to degrade RDX to non-detectable levels in the plant tissue.”
Contaminated
The study confirmed that the plants were able remove and degrade RDX at a rate of 27 kg RDX per hectare. RDX is designated as a priority pollutant by the US Environmental Protection Agency and is of significant and increasing public concern. In the US, over 10 million hectares of military land are contaminated with munitions components, of which, RDX is a major component.
Professor Bruce added: “The recalcitrance of RDX to degradation in the environment, combined with its high mobility through soil and groundwater, mean that plumes of toxic RDX continue to spread below these military sites, threatening drinking water supplies.”
The paper sites an example when in 1997, plumes of RDX pollution were discovered in both groundwater and the aquifer beneath the training range at the Massachusetts Military Reservation in Cape Cod. The aquifer is the sole source of drinking water for half a million people and resulted in the Environment Protection Agency preventing use of all live munitions during training at this site.
The study says that the continuing demand for vast amounts of military explosives means that RDX will continue to be manufactured and used globally on a massive scale for the foreseeable future.
Researchers said that because of the scale of explosives pollution, particularly on military training ranges, there is considerable interest in developing plant-based sustainable remediation strategies.
This research was funded by the Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) of the US Department of Defense and was in collaboration with researchers at the Engineering Research and Development Centre, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and the University of Washington.